The Majapahit empire was the last of the major Hindu empires of the Malay archipelago and is considered one of the greatest states in Indonesian history. Its influence extended to states on Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, Borneo and eastern Indonesia, though the extent of its influence is the subject of debate.
History
After defeating Srivijaya in Sumatra in 1290, Singhasari became the most powerful kingdom in the area. Kublai Khan, the ruler of the Chinese Yuan Dynasty, challenged Singhasari by sending emissaries demanding tribute. Kertanegara, the last ruler of Singhasari, refused to pay the tribute. In 1293, Kublai Khan sent a massive expedition of 1,000 ships to Java.
By that time, Jayakatwang, the Adipati (Duke) of Kediri, a vassal state of Singhasari, had usurped and killed Kertanagara. After being pardoned by Jayakatwang with the aid of Madura's regent, Arya Wiraraja; Raden Wijaya, Kertanegara's son-in-law, was given the land of Tarik timberland. He then opened that vast timberland and built a new village there. The village was named Majapahit, which was taken from a fruit name that had bitter taste in that timberland (maja is the fruit name and pahit means bitter). When Mongolian Yuan army sent by Kublai Khan arrived, Wijaya allied himself with the army to fight against Jayakatwang. Once Jayakatwang was destroyed, Raden Wijaya forced his allies to withdraw from Java by launching a surprise attack. Yuan's army had to withdraw in confusion as they were in hostile territory. It was also their last chance to catch the monsoon winds home; otherwise, they would have had to wait for another six months on a hostile island.
In AD 1293, Raden Wijaya founded a stronghold with the capital Majapahit. The exact date used as the birth of the Majapahit kingdom is the day of his coronation, the 15th of Kartika month in the year 1215 using the Javanese çaka calendar, which equates to November 10, 1293. During his coronation he was given formal name Kertarajasa Jayawardhana. The new kingdom faced challenges. Some of Kertarajasa's most trusted men, including Ranggalawe, Sora, and Nambi rebelled against him, though unsuccessfully. It was suspected that the mahapati (equal with prime minister) Halayudha set the conspiracy to overthrow all of the king's opponents, to gain the highest position in the government. However, after following the death of the last rebel Kuti, Halayudha was captured and jailed for his tricks, and then sentenced to death. Wijaya himself died in AD 1309.
Wijaya's son and successor, Jayanegara was notorious for immorality. One of his sinful acts was taking his own stepsisters as wives. He was entitled Kala Gemet, or "weak villain". In AD 1328, Jayanegara was murdered by his doctor, Tantja. His stepmother, Gayatri Rajapatni, was supposed to replace him, but Rajapatni retired from court to become a bhiksuni (a female Buddhist monk) in a monastery. Rajapatni appointed her daughter, Tribhuwana Wijayatunggadewi, or known in her formal name as Tribhuwannottungadewi Jayawishnuwardhani, as the queen of Majapahit under Rajapatni's auspices. During Tribhuwana’s rule, the Majapahit kingdom grew much larger and became famous in the area. Tribhuwana ruled Majapahit until the death of her mother in AD 1350. She was succeeded by her son, Hayam Wuruk.
Golden Age of Majapahit

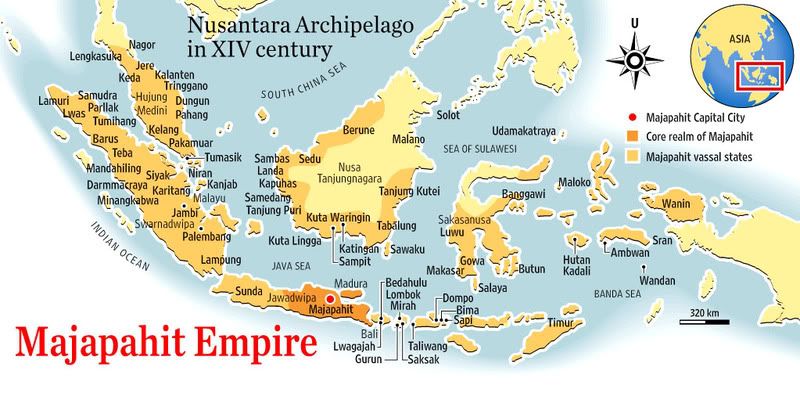
According to the book of Nagarakertagama pupuh (canto) XIII and XIV mentioned several states in Sumatra, Malay Peninsula, Borneo, Sulawesi, Nusa Tenggara islands, Maluku, New Guinea, and some parts of Philippines islands as under Majapahit realm of power. This source mentioned of Majapahit expansions has marked the greatest extent of Majapahit empire.
The Nagarakertagama, written in 1365 depict a sophisticated court with refined taste in art and literature, and a complex system of religious rituals. The poet describes Majapahit as the centre of a huge mandala extending from New Guinea and Maluku to Sumatra and Malay Peninsula. Local traditions in many parts of Indonesia retain accounts in more or less legendary from 14th century Majapahit's power. Majapahit's direct administration did not extend beyond east Java and Bali, but challenges to Majapahit's claim to overlordship in outer islands drew forceful responses.
The nature of the Majapahit empire and its extent is subject to debate. It may have had limited or entirely notional influence over some of the tributary states in included Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, Kalimantan and eastern Indonesia over which of authority was claimed in the Nagarakertagama. Geographical and economic constraints suggest that rather than a regular centralised authority, the outer states were most likely to have been connected mainly by trade connections, which was probably a royal monopoly. It also claimed relationships with Champa, Cambodia, Siam, southern Burma, and Vietnam, and even sent missions to China.
Although the Majapahit rulers extended their power over other islands and destroyed neighboring kingdoms, their focus seems to have been on controlling and gaining a larger share of the commercial trade that passed through the archipelago. About the time Majapahit was founded, Muslim traders and proselytizers began entering the area.
Decline Period of Majapahit
In 1447, Suhita died and was succeeded by Kertawijaya, her brother. He ruled until 1451 AD. After Kertawijaya died, Bhre Pamotan became a king with formal name Rajasawardhana and ruled at Kahuripan. He died in 1453 AD. A three year kingless period was possibly the result of a succession crisis. Girisawardhana, son of Kertawijaya, came to power 1456. He died in 1466 AD and was succeeded by Singhawikramawardhana. In 1468 AD Prince Kertabhumi rebelled against Singhawikramawardhana promoting himself king of Majapahit.
Singhawikramawardhana moved the Kingdom’s capital to Daha and continued his rule until he was succeeded by his son Ranawijaya in 1474 AD. In 1478 AD he defeated Kertabhumi and reunited Majapahit as one Kingdom. Ranawijaya ruled from 1474 AD to 1519 AD with the formal name Girindrawardhana. Nevertheless, Majapahit's power had declined through these family conflicts and the growing power of the north-coastal kingdoms in Java.
Majapahit found itself unable to control the rising power of the Sultanate of Malacca. Dates for the end of the Majapahit Empire range from 1478 (that is, 1400 Saka, the ends of centuries being considered a time when changes of dynasty or courts normally ended) to 1527. The year is marked among Javanese today with candra sengkala "sirna ilang kertaning bumi" (the wealth of earth disappeared and diminished) (sirna = 0, ilang = 0, kerta = 4, bumi = 1). After a series of battles with the Sultanate of Demak, the last remaining courtsmen of Majapahit were forced to withdraw eastward to Kediri; it is unclear whether they were still under the rule of the Majapahit dynasty. This small state was finally extinguished at the hands of the Demak in 1527. A large number of courtiers, artisans, priests, and members of the royalty moved east to the island of Bali; however, the crown and the seat of government moved to Demak under the leadership of Pengeran, later Sultan Fatah[citation needed. The Muslim emerging forces defeated the local Majapahit kingdom in the early 16th century.
Majapahit's Relics





0 comments:
Posting Komentar